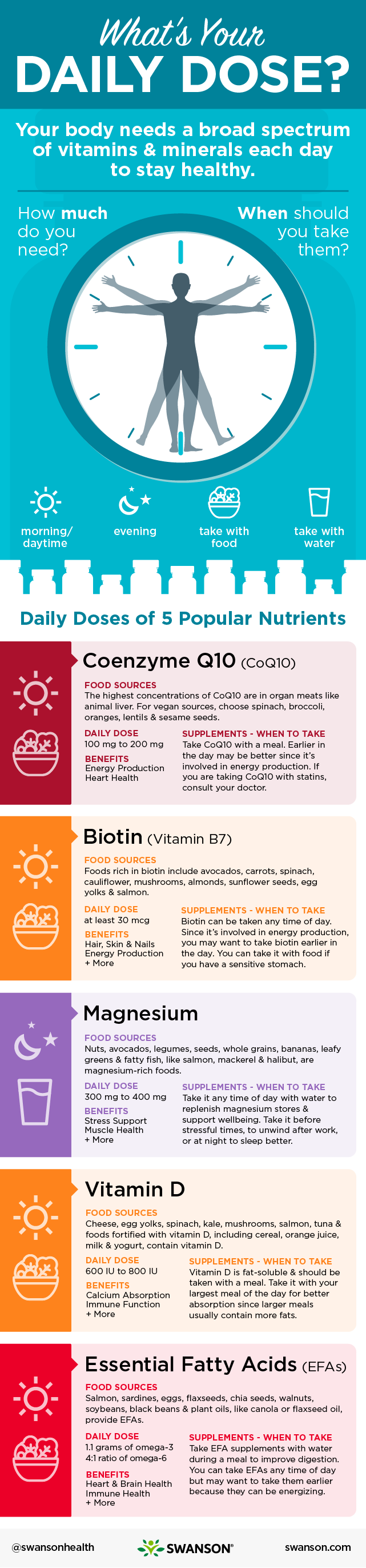
Your body needs a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals each day to stay healthy, but how much do you need? And when should you take them?
We’re here to answer your most frequently asked questions about 5 top nutrients—coenzyme Q10, magnesium, biotin, vitamin D and essential fatty acids—including their core benefits, how much you need, and the best ways to get them.
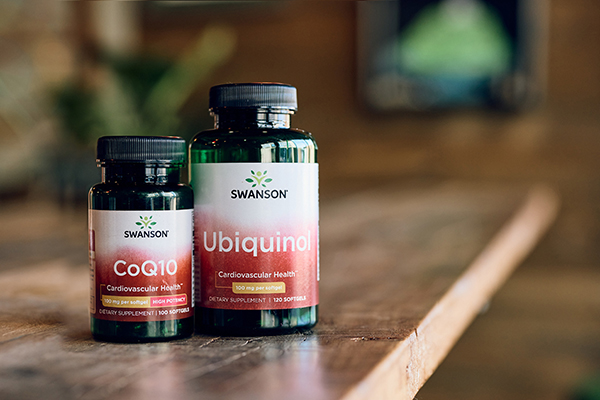
Coenzyme Q10 Benefits
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a vitamin-like antioxidant that our cells need for converting food to energy.1 Your body makes some of it naturally, but CoQ10 levels decline with age.1
Aside from its role in cellular energy production, CoQ10 is best known for promoting cardiovascular health. It is also taken to help minimize muscle-related side effects related to taking statins.1
CoQ10 Daily Dosage
A typical daily dose of CoQ10 is between 100 mg to 200 mg per day, but always follow the directions on your product label unless directed otherwise by your doctor.2 Studies have used doses ranging from 50 mg to 1,200 mg per day in adults, sometimes split into several doses throughout the day.2
What are the best CoQ10 supplements to take? There are two types of CoQ10 supplements—ubiquinol and ubiquinone. Ubiquinol is the active form of CoQ10, and your body converts ubiquinone into ubiquinol.1 Both are great, but younger people may get more benefits from ubiquinone supplements, and older people may benefit more from ubiquinol supplements because of changes to how your body processes ubiquinone as you age.
It is also possible to get some CoQ10 from your diet, but even the best food sources of CoQ10 have fairly small amounts of this nutrient, making supplements the most likely way to meet your daily needs. You can learn about food sources of CoQ10 in the article CoQ10 Food Sources.
When do I Take CoQ10 Supplements?
Most CoQ10 supplement labels say you should take you CoQ10 with both food and water. That’s because CoQ10 is fat-soluble, which means your body absorbs it best when taken with fats or oils. The fats or oils in the foods you eat serve as carriers for the CoQ10. And since CoQ10 is involved in cellular energy production, you may prefer to take your CoQ10 with a healthy breakfast. If you are taking CoQ10 with statins, talk with your doctor about the best time to take your CoQ10 supplement.
Magnesium Benefits
Magnesium is a relaxing, stress-relieving, revitalizing mineral that your body needs to carry out hundreds of vital processes. It’s involved in everything from energy production to muscle and nerve function, blood pressure regulation, calcium absorption and more.3
According to studies, most people have low levels of magnesium either due to their diets or soil depletion of magnesium.4 Not getting enough magnesium can cause a host of health concerns, many of which are easily mistaken for something else—like feeling stressed, anxious or fatigued.3,5
Replenishing your body’s stores of magnesium can help you have more energy, sleep better, reduce stress, support healthy bones and heart function, and promote overall wellness.3,6 Take a deeper dive into the many benefits of magnesium in the article Magnesium Benefits & Uses and Magnesium for Sleep.
Magnesium Daily Dosage
Most adults need between 300 mg to 400 mg of magnesium each day, but when you get stressed your body wastes magnesium, so then you may need more.3,6 And it’s also important to know that we only absorb 30% to 40% of the magnesium we consume.3
There are many different types of magnesium supplements—from highly absorbable chelated magnesium supplements to our replenishing Mellow Mag magnesium drink. Read What is the Best Magnesium Supplement Form for You? to learn more about all the different forms of magnesium and their benefits.
When do I Take Magnesium Supplements?
The time of day you take magnesium may depend on why you are taking it. If your goal is to replenish magnesium levels for overall wellness, you can take your magnesium supplement at a time of day when you’re most likely to remember to take it. But be sure to read and follow the instructions on your product label. Some supplements, like Swanson Ultra Chelated Magnesium, should be taken three times per day with water, and your product instructions may vary.
If you are looking for magnesium’s stress-reducing benefits you may consider taking it before your most stressful time of day or at the end of a stressful day to help you unwind. Similarly, if you’re taking magnesium to help you relax so you can sleep better, you may want to take it in the evening before bed.
Biotin Benefits
Biotin is at the top of our list of beautifying nutrients. It has such an excellent reputation for its hair- and skin-supporting benefits that it was once known as vitamin H, after the German words "haar" and "haut," which mean "hair" and "skin" respectively.7 And it supports healthy nail growth too!
Biotin is also known as vitamin B-7 and it’s an important member of the B-complex family of vitamins, all of which work together to energize and support wellbeing. Biotin plays a role in the metabolism of fatty acids, glucose and amino acids, as well as cell signaling, gene regulation and more.8
You can learn about the benefits of all the B-complex vitamins in Your Complete Guide to B Vitamins and take a deeper dive into the benefits of biotin in Biotin Benefits for Every Body.
Biotin Daily Dosage
The Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) recommends that healthy adults get at least 30 mcg of biotin per day.8 Some foods contain biotin, including organ meats, eggs, fish, meat, seeds and nuts.8
When you can’t get enough biotin from food sources each day, get the next best thing in Swanson Real Food Biotin—a biotin supplement derived from real food sources.
When do I Take Biotin Supplements?
Biotin is water-soluble and can be taken any time of day. Since this B vitamin is involved in energy production, it may be best to take it earlier in the day. You don’t need to take biotin with food, but you can take it with a meal if it helps you remember to take it or if your stomach is generally sensitive to supplements.
Vitamin D Benefits
Vitamin D is also known as the sunshine vitamin since our bodies make some vitamin D after exposure to the sun.9 But that doesn’t mean you don’t need a vitamin D supplement. In fact, most of us don’t get enough vitamin D.10 That’s either because we aren’t outside enough every day, or because we dutifully wear sunscreen when we are in the sun. Plus, as we age, our skin can’t synthesize vitamin D as efficiently as it did when we are younger.9
Why does vitamin D matter? Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium and phosphate absorption, which is needed to maintain bone health.9 Without vitamin D, calcium can’t do its job to help keep our bones healthy and strong! Vitamin D also plays a role in immune function and neuromuscular health.9
Vitamin D Daily Dosage
Adults between 18 to 70 years old need at least 600 IU of vitamin D per day.9 After age 70, you need more—at least 800 IU per day. Since very few foods contain vitamin D naturally, taking a vitamin D supplement is your best bet for meeting your daily requirements.
Experts say that the best type of vitamin D supplement may be vitamin D3, which may be twice as effective as other supplements for raising vitamin D levels.10 Try it in Swanson Premium Vitamin D-3 Highest Potency, or get the winning combo of calcium and vitamin D in Swanson Premium Calcium Citrate & Vitamin D.
When do I Take Vitamin D Supplements?
Vitamin D is fat-soluble and best taken with a meal containing fats or oils. The time of day you take your vitamin D isn’t as important as just remembering to take it, so pair it with a meal when you’re most likely to remember. Since breakfast can be rushed for some people, especially through the week, breakfast may not be the best choice. Also, taking it with your largest meal of the day may be better, since larger meals will likely contain more fats or oils.
Essential Fatty Acid Benefits
There’s a reason 18.8 million adults take an omega-3 supplement, and you should too—essential fatty acids (EFAs) truly are essential.11 EFAs, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, support heart and brain health, promote healthy joints and skin, immune health, energy and more.12
Everyone needs essential fatty acids, but they may become even more important the older we get. European researchers have estimated that nearly 16 billion dollars (or 12.9 billion euros) in medical costs could be saved if everyone over 55 took an omega-3 fatty acid supplement.12 How’s that for essential?
You might hear more about omega-3 fatty acids than omega-6, but a balance of both is important for maintaining optimal health. They work together to support wellbeing.
Essential Fatty Acid Daily Dosage
How much omega-3 and omega-6 do you need each day? Healthy adults need at least 1.1 grams of omega-3 fatty acids per day.13 The high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio that is common in Western diets can be detrimental to health.14 Research shows that reducing the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 to 4:1 can significantly improve health, though ratios closer to 1:4 are optimal.14
To achieve a 4:1 ratio, if your intake of omega-3 is 1.1 grams per day, you’d want to balance that with no more than 4.4 grams of omega-6. But if you already get more than 4.4 grams of omega-6 fatty acids from dietary sources, you may want to increase your omega-3 intake to achieve a 4:1 ratio. It’s a good idea to talk with your doctor about the supplements you take and always follow the directions on your product label unless otherwise directed by a physician.
Most omega-3 fatty acid supplements are derived from marine sources, with fish oil supplements being the most common. For a vegan source of omegas, try our award-winning Plant Based Omega-3 formula, which was named 2018 Omega-3 Product of the Year by NutraIngredients USA. You can also get omega-3 from krill oil supplements, and your body may more easily absorb the omega-3s from krill oil than omega-3s from fish oil.15
Evening primrose oil and black currant seed oil are excellent sources of omega-6 fatty acids, including gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), which is essential for skin and hair growth.16
When do I Take Essential Fatty Acid Supplements?
Most EFA product labels suggest taking the supplement with water during a meal to improve digestion of the EFAs. The meal you take it with is up to you, but since fatty acids can be energizing, you may choose to take them earlier in the day. Some EFA supplements are designed to be taken multiple times per day. So, as always, be sure to read and follow the instructions on your product label.
Your Daily Dose of Wellness
It’s important to get balanced nutrition every single day, yet navigating the world of wellness to decide how much you need of each nutrient can get overwhelming sometimes. We hope this article, and the many others we share, will help you along your journey and enable you to make educated decisions about your nutritional routines.
Would you like to learn your doses of even more essential nutrients? Let us know in the comments below! And sign up for Swanson Health emails so you’ll be the first to know about new wellness resources, innovative products and valuable promotions.

About Lindsey Toth, MS, RD
Registered Dietitian, Swanson Health
Lindsey is a nationally recognized registered dietitian and nutritionist with a soft spot for ice cream. She empowers people to take charge of their health by finding the balance between the pleasure and nourishment in food.
Her philosophy is that you should take care of your body because it’s the only permanent home you have. It’s what inspired her to pursue a career in nutrition and, ultimately, led her to Swanson Health.
Sources:
1 CoQ10: What are the Heart Health Benefits? Cleveland Heart Lab. http://www.clevelandheartlab.com/blog/horizons-coq10-what-are-the-heart-health-benefits/ (Accessed 08/04/2018)
2 Coenzyme Q10: CoQ10. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-coenzymeq10-coq10#1 (Accessed 08/04/2018)
3 Magnesium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals: National Institutes of Health. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/ (Accessed 11/30/2017)
4 Magnesium deficiency in plants: An urgent problem. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221451411500121X (07/17/2018)
5 Association between magnesium intake and depression and anxiety in community-dwelling adults: the Hordaland Health Study. PubMed https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19085527 (Accessed 2/15/2018)
6 Magnesium and the Brain: The Original Chill Pill. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/evolutionary-psychiatry/201106/magnesium-and-the-brain-the-original-chill-pill (07/17/2018)
7 Vitamin H. The Dermal Institute. http://www.dermalinstitute.com/us/library/94articleVitaminH.html (Accessed 3/2/2018)
8 Biotin. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. National Institutes of Health. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Biotin-HealthProfessional/ (Accessed 2/26/2018)
9 Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. National Institutes of Health. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional (Accessed 07/11/2018)
10 Vitamin D deficiency soars in the U.S., study says. Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/vitamin-d-deficiency-united-states (Accessed 07/11/2018)
11 Most Used Natural Products. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. https://nccih.nih.gov/research/statistics/NHIS/2012/natural-products/omega3 (Accessed 07/23/2018)
12 Omega-3 supplementation could save EU 12.6bn a year in heart disease spending. NutraIngredients. https://www.nutraingredients.com/Article/2016/05/10/Omega-3-supplements-could-save-EU-billions-in-heart-disease-spending (Accessed 07/11/2018)
13 Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/ (Accessed 08/04/2018)
14 The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. PubMed. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12442909 (Accessed 08/04/2018)
15 The Health Benefits of Krill Oil versus Fish Oil. University of Washington. http://depts.washington.edu/nutr/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Krill-vs-Fish-Oil2012.pdf (Accessed 1/29/2018)
16 GLA: Fit for a King? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/gla-fit-for-a-king (Accessed 07/27/2018)
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.



